Pagets Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
Paget's Disease: A Comprehensive overview
Paget's Disease is an idiopathic condition of abnormal bone remodeling with normal bone being replaced through an active interplay between excessive bone resorption and abnormal new bone formation. Learn more about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Epidemiology
Demographics:
- Peak incidence in the 5th decade of life
- Common in Caucasians (northern European / Anglo-Saxon descent)
- Males = females
Anatomic location:
- May be monostotic or polyostotic
- Common sites include femur, pelvis, tibia, skull, and spine
Etiology
Pathophysiology:
- Increased osteoclastic bone resorption is the primary cellular abnormality
- Cause is thought to be a slow virus infection (intra-nuclear nucleocapsid-like structure)
- Paramyxovirus
- Respiratory syncytial virus
Genetics:
- Most cases are spontaneous
- Hereditary
- Familial clusters have been described with ~40% autosomal dominant transmission
Clinical Presentation
Most patients with Paget's disease are asymptomatic. Symptomatic patients may present with:
- Bone pain
- Fractures
- Deformities
- Headache
- Hearing loss
- Neurologic symptoms (if spinal involvement)
Diagnosis
Diagnostic tests:
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) level: Elevated in up to 90% of patients (marker of increased bone turnover)
- X-rays: Show a widened bone and areas of sclerosis
- Bone scan: Shows increase in activity and uptake
- Biopsy: Not usually needed for diagnosis, reserved for atypical cases or suspicion of malignancy
Treatment
Non-pharmacological:
- Physical therapy for pain relief and to strengthen muscles around affected bones
- Assistive devices (cane, walker) for mobility and to reduce risk of falls
- Weight-bearing exercises to maintain bone strength
Pharmacological:
- Bisphosphonates (e.g. alendronate, risedronate) to reduce bone resorption
- Calcitonin to inhibit bone resorption
- Pain medications (NSAIDs, acetaminophen) for pain relief
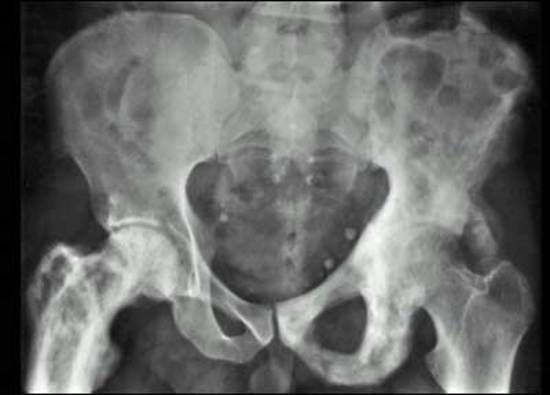
X-ray showing the characteristic bone changes in Paget's disease.
Prognosis
With appropriate treatment, most patients with Paget's disease have a good prognosis and can live normal lives. However, complications such as fractures and deformities can occur if the disease is not properly managed.

