Tarsal Coalition: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Learn about tarsal coalition, a condition where abnormal bone fusion in the foot causes pain and discomfort. This comprehensive guide covers its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options available, from physical therapy to surgery. Whether you're an athlete seeking performance-enhancing treatments or a concerned parent, this article provides valuable insights into managing this condition effectively
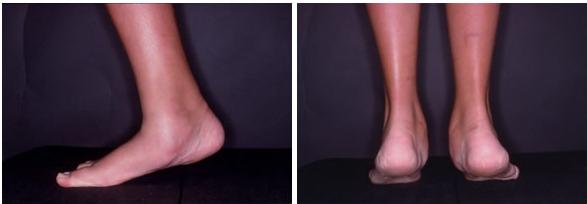 Tarsal coalition is a condition characterized by abnormal fusion or connection between two or more bones in the foot. It can cause pain, discomfort, and limited mobility, affecting both adults and children. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options available for tarsal coalition. Whether you're an athlete seeking performance-enhancing treatments or a concerned parent, this article will provide valuable insights into managing this condition effectively.
Tarsal coalition is a condition characterized by abnormal fusion or connection between two or more bones in the foot. It can cause pain, discomfort, and limited mobility, affecting both adults and children. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options available for tarsal coalition. Whether you're an athlete seeking performance-enhancing treatments or a concerned parent, this article will provide valuable insights into managing this condition effectively.
Understanding Tarsal Coalition
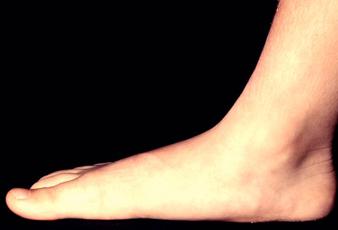 Tarsal coalition typically occurs when there is an abnormal fusion between two specific bones in the foot. The most common sites of fusion include the calcaneus, talus, and navicular bones. This fusion restricts normal movement and can lead to pain and discomfort. The condition can be congenital, meaning it is present from birth, or it can develop later due to trauma or repetitive stress.
Tarsal coalition typically occurs when there is an abnormal fusion between two specific bones in the foot. The most common sites of fusion include the calcaneus, talus, and navicular bones. This fusion restricts normal movement and can lead to pain and discomfort. The condition can be congenital, meaning it is present from birth, or it can develop later due to trauma or repetitive stress.
Causes of Tarsal Coalition
The exact causes of tarsal coalition are not fully understood. However, research suggests that genetic factors and developmental abnormalities play a significant role. For some individuals, the condition may be present at birth and become symptomatic later in life. In other cases, an injury or overuse can trigger the fusion process, leading to tarsal coalition.
Common Symptoms of Tarsal Coalition
Tarsal coalition may cause a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the severity and location of the fusion. Some common symptoms include:
- Persistent foot or ankle pain, especially during physical activity.
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the affected foot.
- Fatigue or muscle cramps in the leg or foot.
- Flatfoot or high arches.
- Tiredness or aching in the affected foot after standing or walking for extended periods.
Diagnosis of Tarsal Coalition
Proper diagnosis of tarsal coalition involves a thorough evaluation by a medical professional specializing in foot and ankle conditions. The diagnosis typically includes:
- Medical history review to identify any previous injuries or symptoms.
- Physical examination to assess foot structure, range of motion, and areas of tenderness.
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, to visualize the fusion and its extent accurately.
Treatment Options for Tarsal Coalition
1. Conservative Treatment:
- Physical therapy: Targeted exercises and stretching routines to improve flexibility and strengthen supporting muscles.
- Pain management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or cortisone injections for pain relief.
- Orthotic devices: Custom-made shoe inserts or braces to provide support and reduce discomfort.
2. Surgical Treatment:
- Resection surgery: Removal of the abnormal bony connection to restore normal foot function.
- Arthrodesis surgery: Fusion of the affected bones to stabilize the foot and relieve pain.
- Minimally invasive surgery: Less invasive techniques using specialized instruments for faster recovery and minimal scarring.
- Arthroscopic surgery: Utilizing a tiny camera and small incisions to visualize and treat the coalition.
- Open surgery: Traditional surgical approach for complex or severe cases.
Recovery and Prognosis
Recovery time and long-term prognosis after tarsal coalition treatment can vary depending on the chosen treatment method, the severity of the condition, and individual factors. Following surgery, a period of rest, rehabilitation exercises, and physical therapy is usually recommended to regain strength, flexibility, and mobility. The success rate of tarsal coalition surgery is generally high, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved functionality.
Conclusion
Tarsal coalition is a condition that can significantly impact the quality of life, especially for those who lead an active lifestyle. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, and exploring the available treatment options are crucial steps in effectively managing tarsal coalition. Whether through conservative measures or surgical interventions, relief from pain and restoration of normal foot function is possible. Consulting with a healthcare professional specializing in foot and ankle conditions is the first step towards finding the most suitable treatment approach for individual needs.
Remember, early intervention and proactive management can make a significant difference in overcoming the challenges posed by tarsal coalition. Take control of your foot health and explore the options available to reclaim an active, pain-free lifestyle.

