Understanding the Anatomy of the Popliteal Fossa: Boundaries and Contents
Discover the diamond-shaped depression behind the knee that forms an area of transition between thigh and leg. Learn about the boundaries and contents of the popliteal fossa.
The popliteal fossa is a diamond shaped depression behind the knee. It forms an area of transition between the thigh and the leg through which arteries, veins, and nerves pass through. In this blog post, we will discuss the boundaries and contents of the popliteal fossa.
The diamond-shaped fossa is formed between the muscles of the posterior compartments of the thigh and the leg. The superior medial boundary of the popliteal fossa is formed by the distal ends of the semimembranosus and the semitendinosus muscle. The superior laterally boundary is formed by the biceps femoris muscle. The inferomedial boundary is formed by the medial head of the gastrocnemius, and the inferolateral boundary is formed by the plantaris and the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle. In terms of the floor, it's comprised of the capsule of the knee joint and the oblique popliteal ligament, as well as the fascia of the popliteal muscle and the popliteal surface of the femur.
In terms of the roof of the popliteal fossa, this is formed by skin, superficial fascia, and deep fascia. The most important structure to remember with regard to the roof is the small saphenous vein. The small saphenous vein passes through the roof, receives its blood supply from the dorsal venous arch of the foot, and passes between the heads of the gastrocnemius muscles to drain into the popliteal vein.
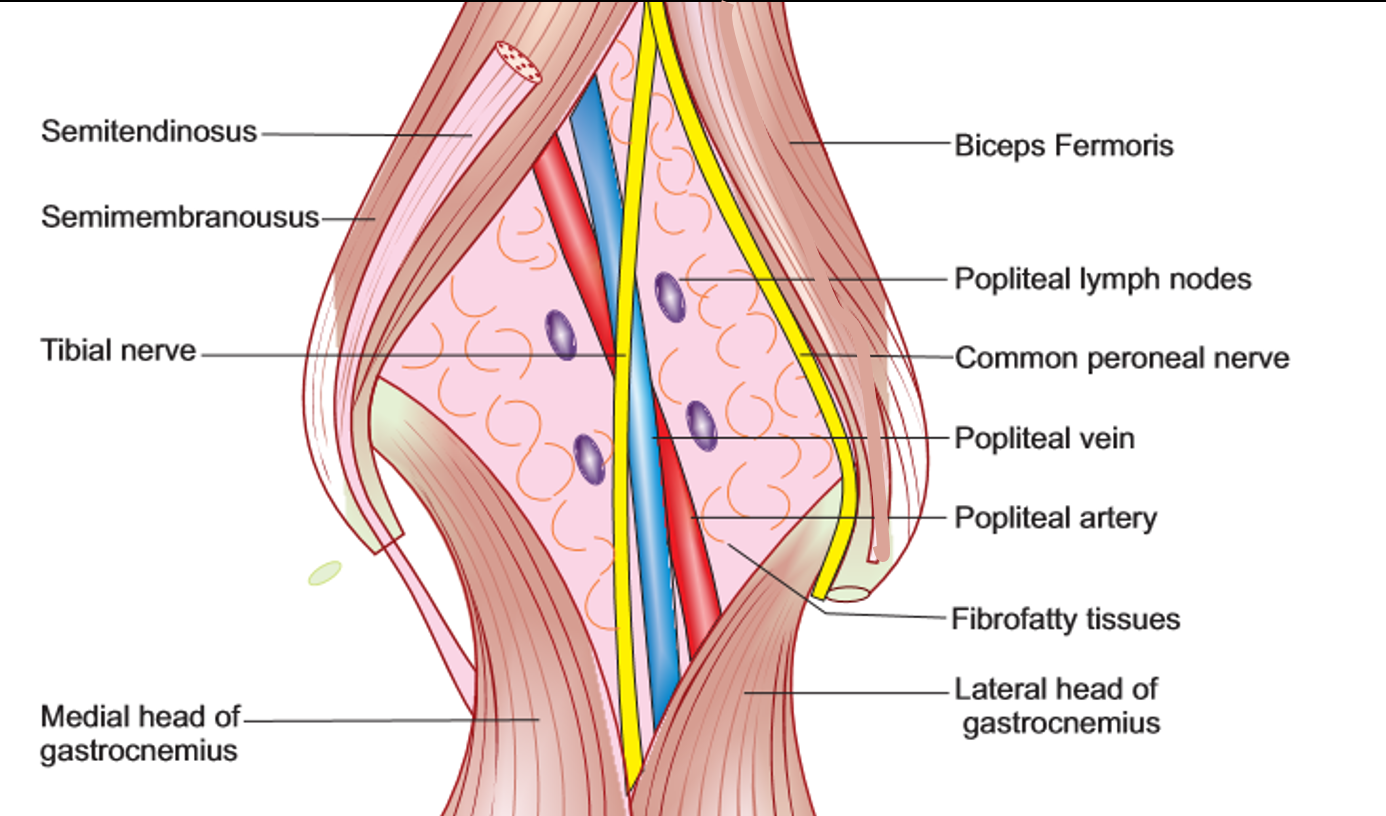
Now let's take a look at some of the contents of the popliteal fossa. It contains four main structures: the popliteal artery, the popliteal vein, the tibial nerve, and the common perineal nerve. The tibial nerve and the common peroneal nerves are branches of the sciatic nerve.
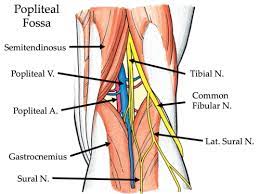
The popliteal artery is the deepest structure in the popliteal fossa. It's a continuation of the superficial femoral artery and divides into the tibio-peroneal trunk and the anterior tibial artery. The popliteal vein is superficial to the popliteal artery and exits the popliteal fossa superiorly, passing through the adductor hiatus within the adductor magnus muscle to enter the anterior compartment of the thigh. It receives blood from the anterior and posterior tibial veins and drains to the femoral vein.
That's the anatomy of the popliteal fossa. Understanding its boundaries and contents is important for medical professionals dealing with injuries or conditions affecting this area.

