Understanding the Muscles of the Anterior and Lateral Compartments of the Leg
This article provides detailed information about the muscles of the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg, their functions, and their innervation.
This article is aimed at providing a comprehensive understanding of the muscles of the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg, their functions, and their innervation.
Table of Contents
- Muscles of the Anterior Compartment
- Muscles of the Lateral Compartment
- Innervation of the Muscles of the Anterior and Lateral Compartments
- Functions of the Muscles of the Anterior and Lateral Compartments
Muscles of the Anterior Compartment
The anterior compartment of the leg consists of four muscles that mainly act to dorsiflex, extend to the toes, and to invert the foot. These muscles are:
| Muscle | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Tibialis Anterior | Dorsiflexion, inversion of the foot | 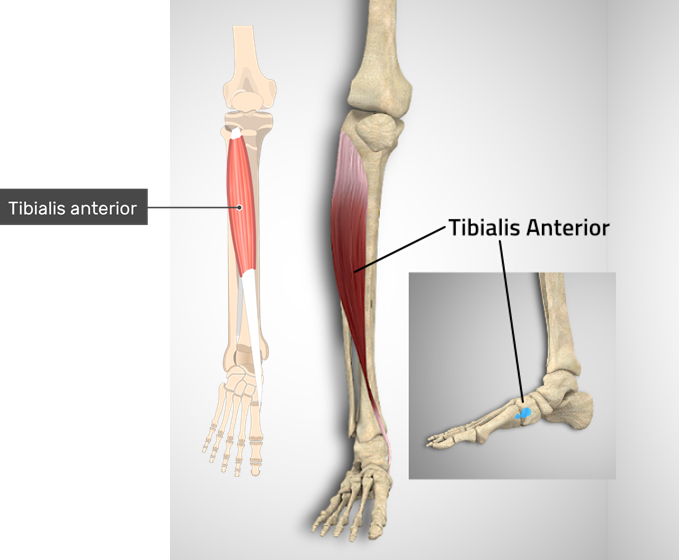 |
| Extensor Hallucis Longus | Extension of the big toe | 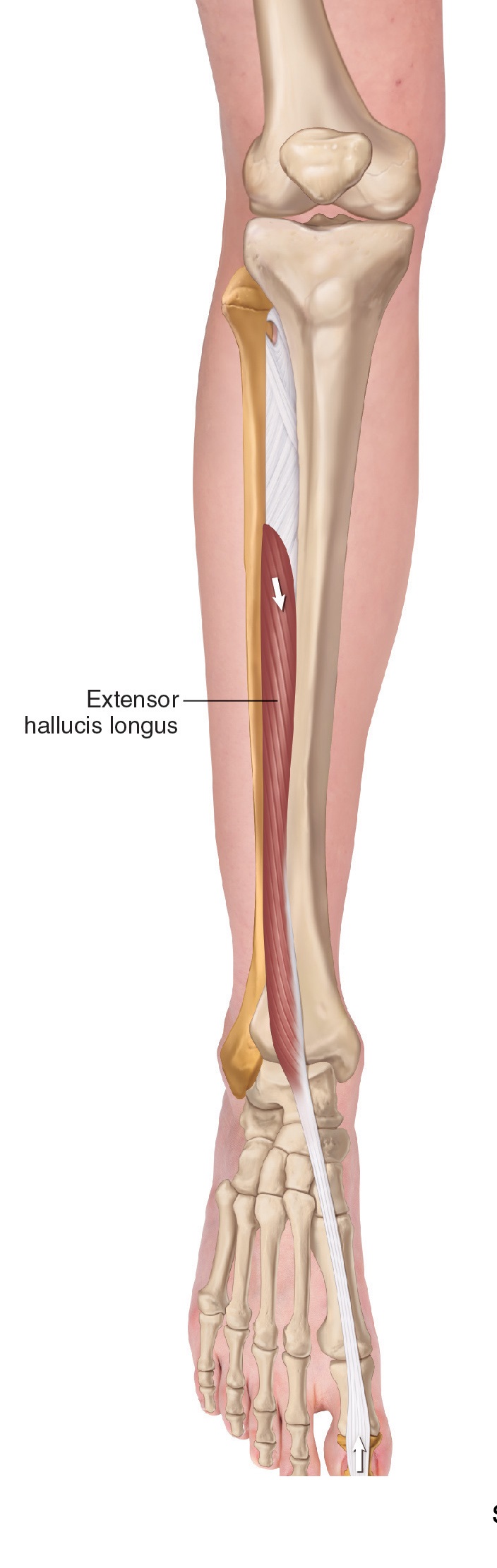 |
| Extensor Digitorum Longus | Extension of the four toes |  |
| Fibularis Tertius | Dorsiflexion, eversion of the foot |  |
Muscles of the Lateral Compartment
The lateral compartment of the leg contains only two muscles that mainly act to evert the foot. These muscles are:
| Muscle | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Peroneus Longus (Fibularis Longus) | Eversion of the foot, support of the arches of the foot |  |
| Peroneus Brevis (Fibularis Brevis) | Eversion of the foot |  |
Innervation of the Muscles of the Anterior and Lateral Compartments
The anterior compartment of the leg is supplied by the deep branch of the common fibular nerve, while the lateral compartment is supplied by the superficial branch of the same nerve.
Functions of the Muscles of the Anterior and Lateral Compartments
The muscles of the anterior compartment mainly act to dorsiflex the foot, extend the toes, and to invert the foot. Conversely, the muscles of the lateral compartment primarily act to evert the foot. However, the tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior, and peroneus longus muscles contribute to arch support due to their medial attachment to the foot. These muscles play a crucial role in maintaining the stability, flexibility, and overall movement of the lower limb.
Knowing the anatomy and function of these muscles is crucial in sports, physical therapy, and other related fields. A good understanding of the muscles can help identify and treat injuries or imbalances that may occur, leading to better treatment and faster recovery of patients.
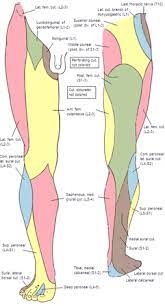
Nerve Supply to the Anterior and Lateral Compartments
The common fibular nerve, a branch of the sciatic nerve, supplies the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg. The nerve splits into two branches at the popliteal fossa, the deep and superficial branches. The deep branch supplies the anterior compartment while the superficial branch supplies the lateral compartment.
Conclusion
Understanding the muscles of the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg and their innervation is crucial for anyone interested in anatomy or physical therapy. By knowing the anatomy and function of these muscles, you can better understand the mechanism of injuries or imbalances that may occur, leading to better treatment and faster recovery of patients. This article provides in-depth information about these muscles to help you gain a better understanding of this portion of human anatomy..

