"Explore the Wonders of the Carpal Bones: From Scaphoid to Hamate"
Dive into the intricacies of the carpal bones and learn about their functions, common fractures, and clinical significance.
The Carpal Bones
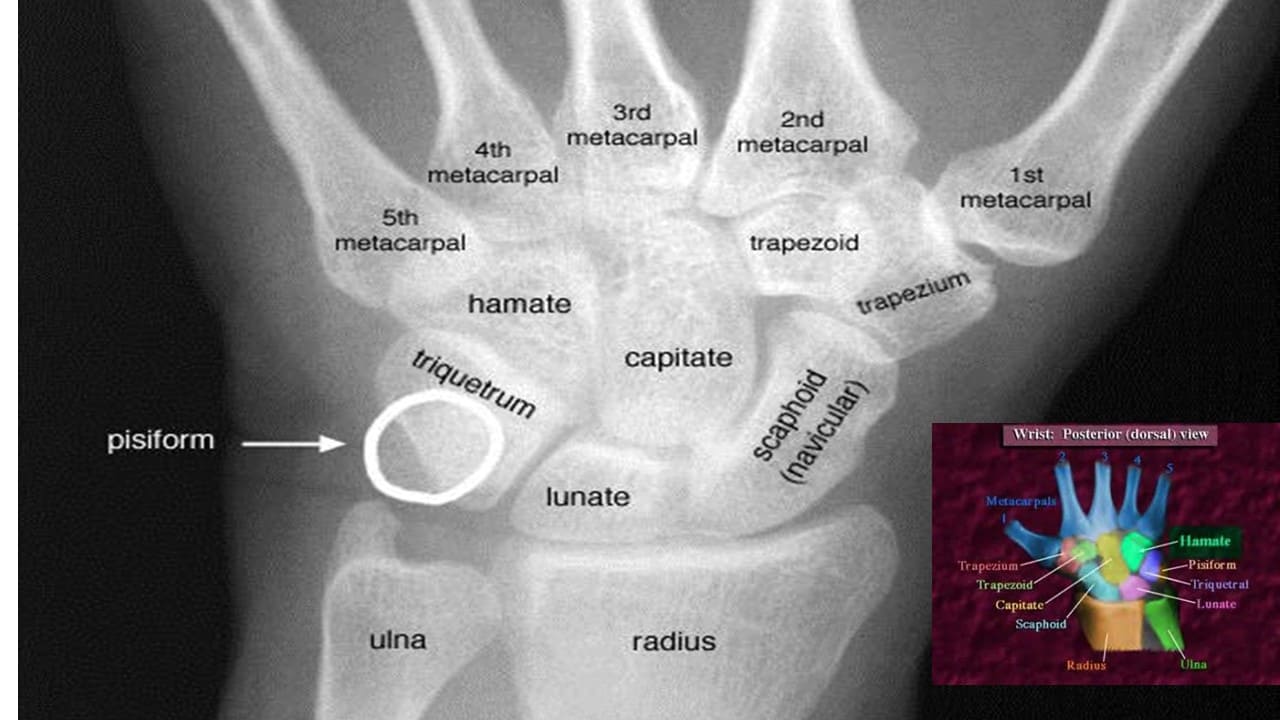
Mnemonic
A useful mnemonic to help remember the carpal bones is shown below:
Some – Scaphoid
Lovers – Lunate
Try – Triquetrum
Positions – Pisiform
That – Trapezium
They – Trapezoid
Can’t – Capitate
Handle – Hamate
Scaphoid
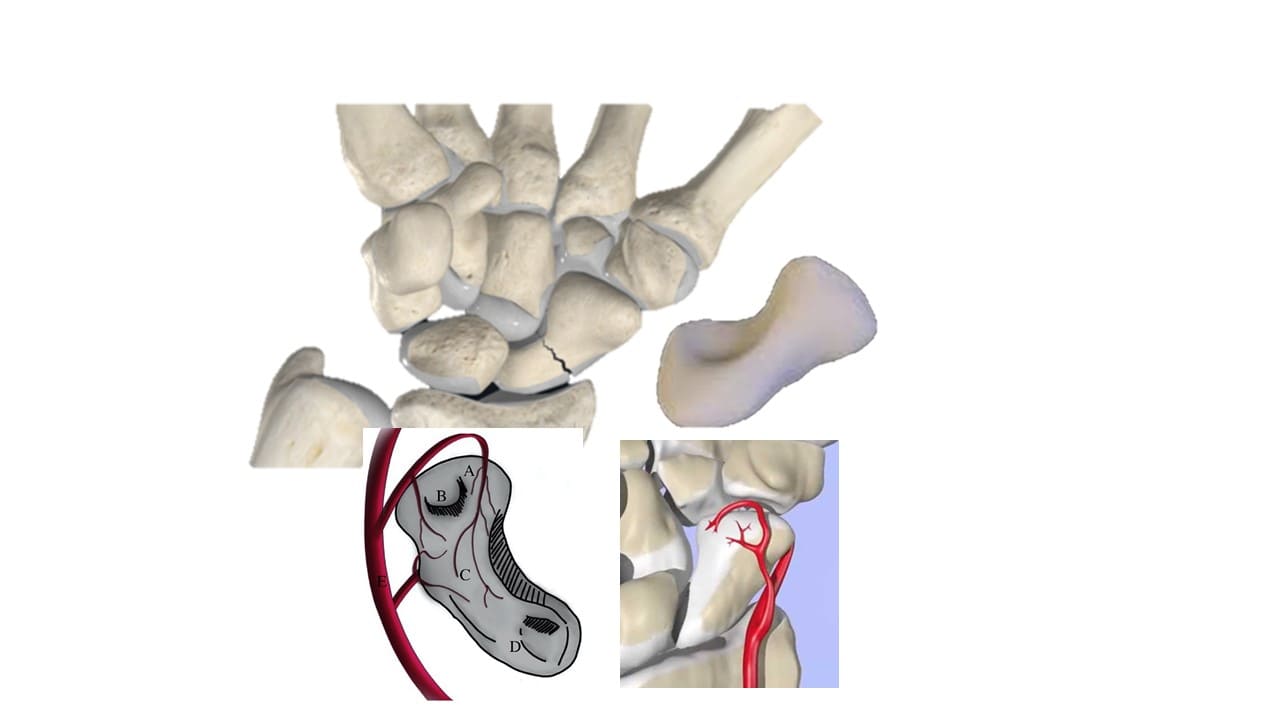
Scaphoid (“boat-shaped”) is a boat-shaped bone which articulates proximally with the radius to form the radial border of the carpal tunnel.
The scaphoid is the largest bone in the proximal row of carpal bones and is also the most commonly fractured. It often occurs due to a fall on an outstretched hand. As a result of the poor blood supply to the scaphoid, fractures can be slow to heal and avascular necrosis of the proximal fragment of the scaphoid can occur.
Lunate
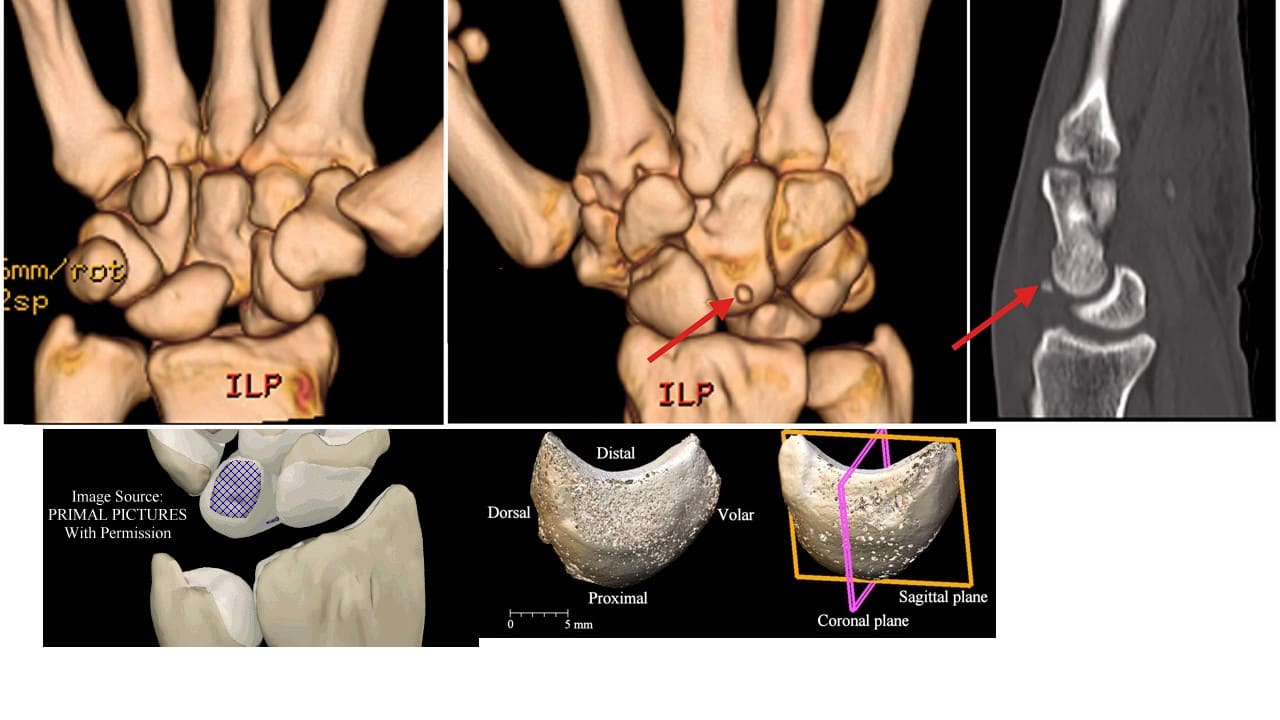
Lunate (“moon-shaped”) is a crescent-shaped bone articulating proximally with the radius. The lunate is found centrally in the carpal bones between the scaphoid and triquetrum. The lunate bone is the most frequently dislocated carpal bone.
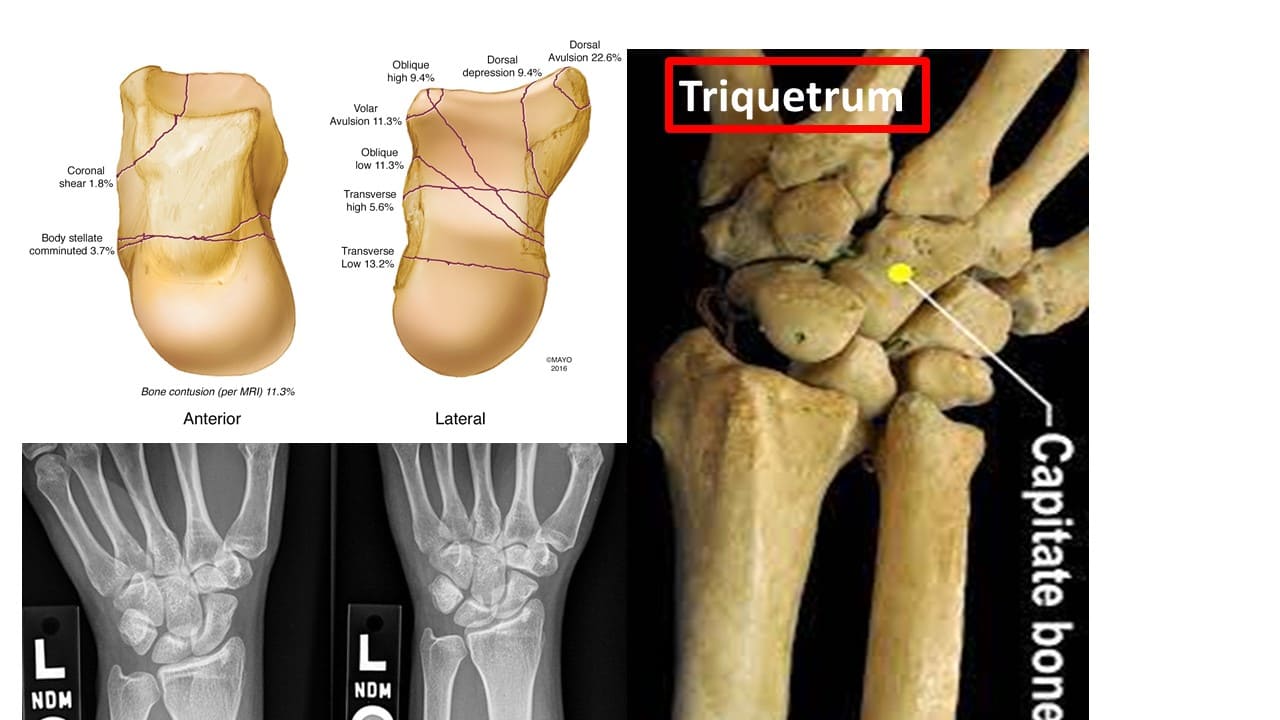
Triquetrum
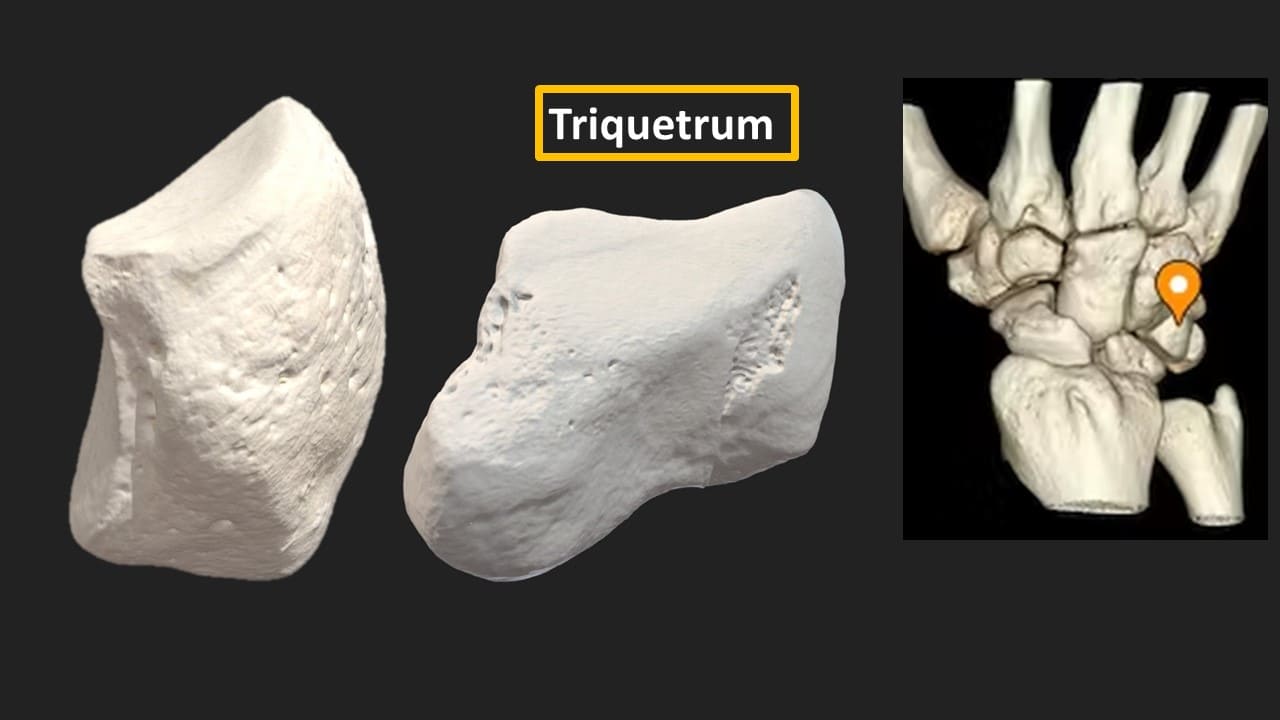
Triquetrum (“three-cornered”) is a pyramidal bone. The triquetrum lies between the lunate and pisiform bones on the medial side of the proximal row of carpal bones. Fractures of the triquetrum often occur upon forceful dorsiflexion of the hand such that an avulsion fracture occurs on the dorsal aspect of the bone.
Pisiform
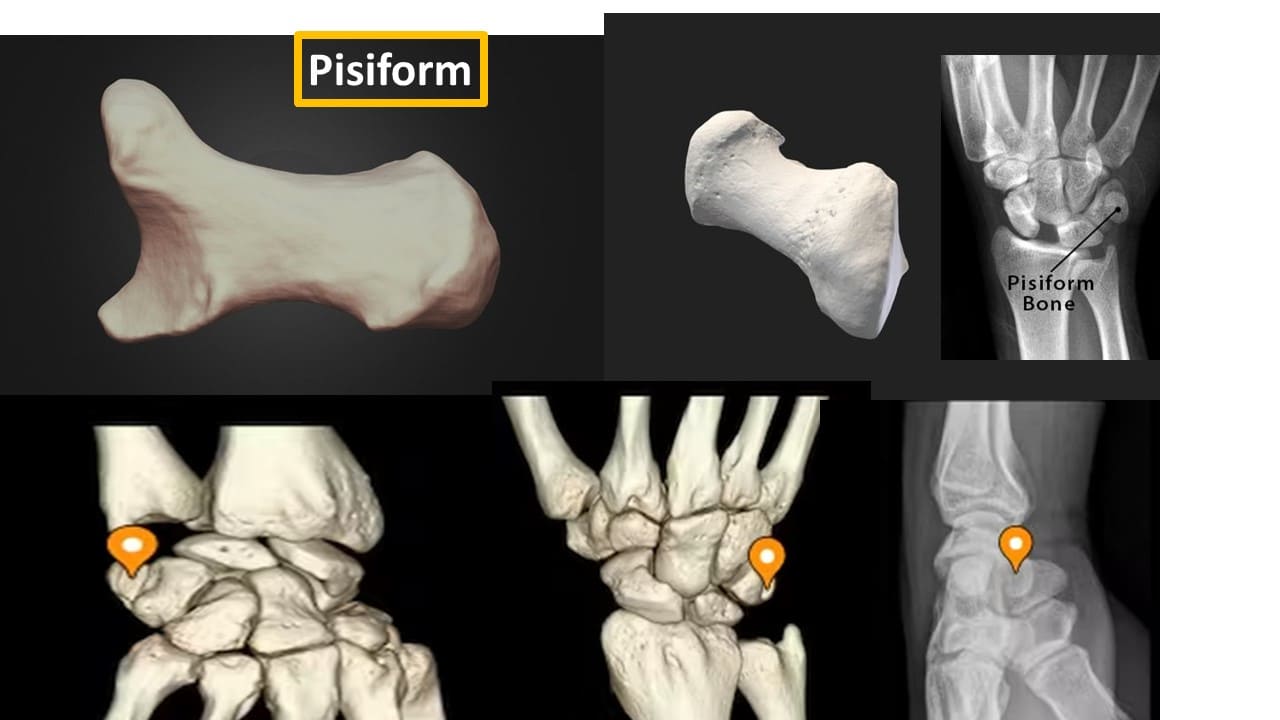
Pisiform (“pea-shaped”) is a small round sesamoid bone found in the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris. The pisiform articulates with the anterior surface of the triquetrum bone, therefore extending anteriorly to form the bump that can be felt at the medial base of the hand. The pisiform bone forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel. In contrast to the other carpal bones, the pisiform is not involved in movements of the wrist.
Trapezium
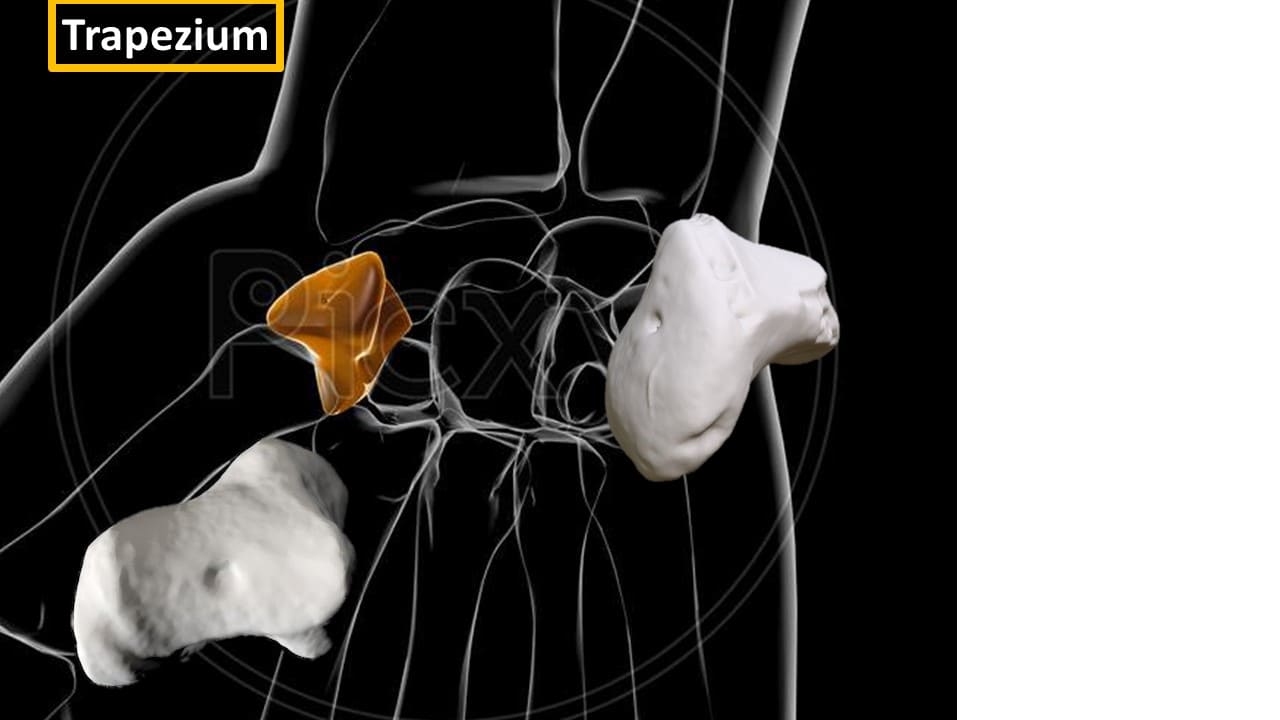
Trapezium (“table”) is a four-sided bone. It articulates with four bones; the 1st and 2nd metacarpals, the scaphoid and the trapezoid. The trapezium has a distinct tubercle on the palmar surface which projects anteriorly.
Trapezoid
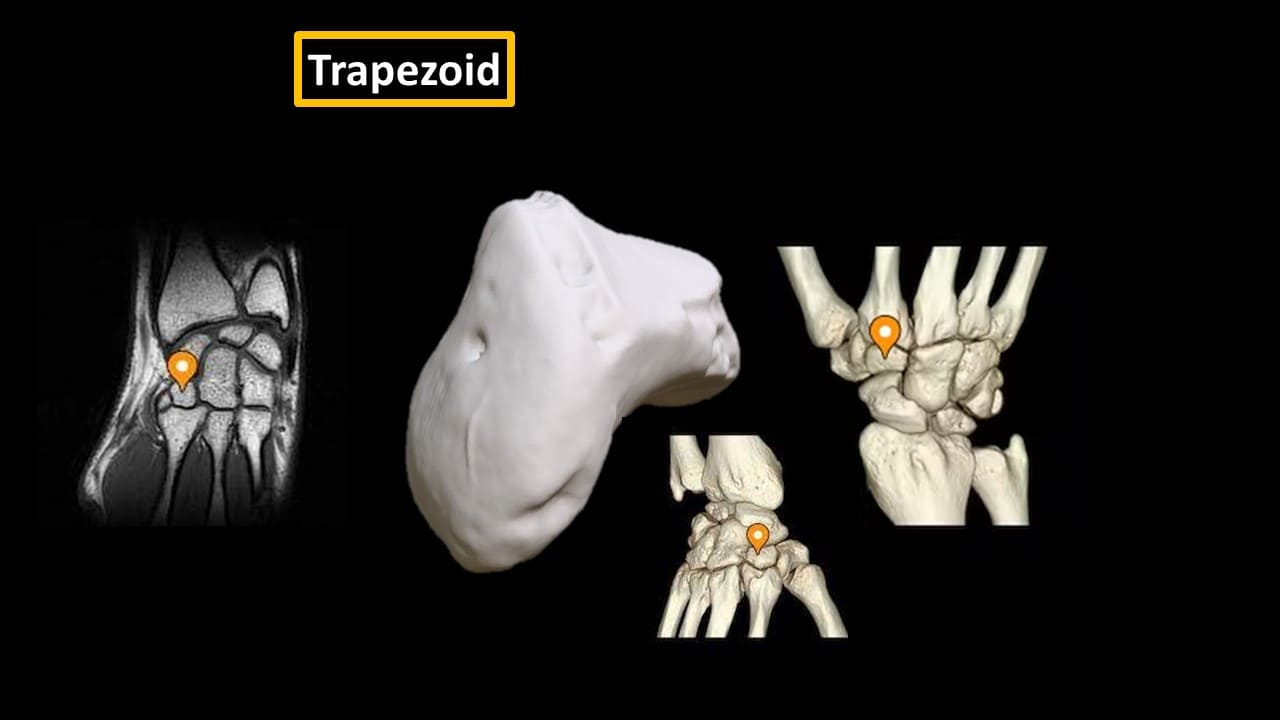
The trapezoid (“resembles a table”) is a wedge-shaped bone. It gets its name due to its similarity to the trapezium. The trapezoid is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones. The trapezoid articulates with four bones; the 2nd metacarpal, the trapezium, the capitate and the scaphoid bone. The trapezoid is the least commonly fractured carpal bone.
Capitate
Capitate (“head-shaped”) is a head-shaped bone. The capitate is the largest carpal bone and articulates with five bones; the 3rd metacarpal, the trapezoid, scaphoid, lunate and hamate.
Hamate
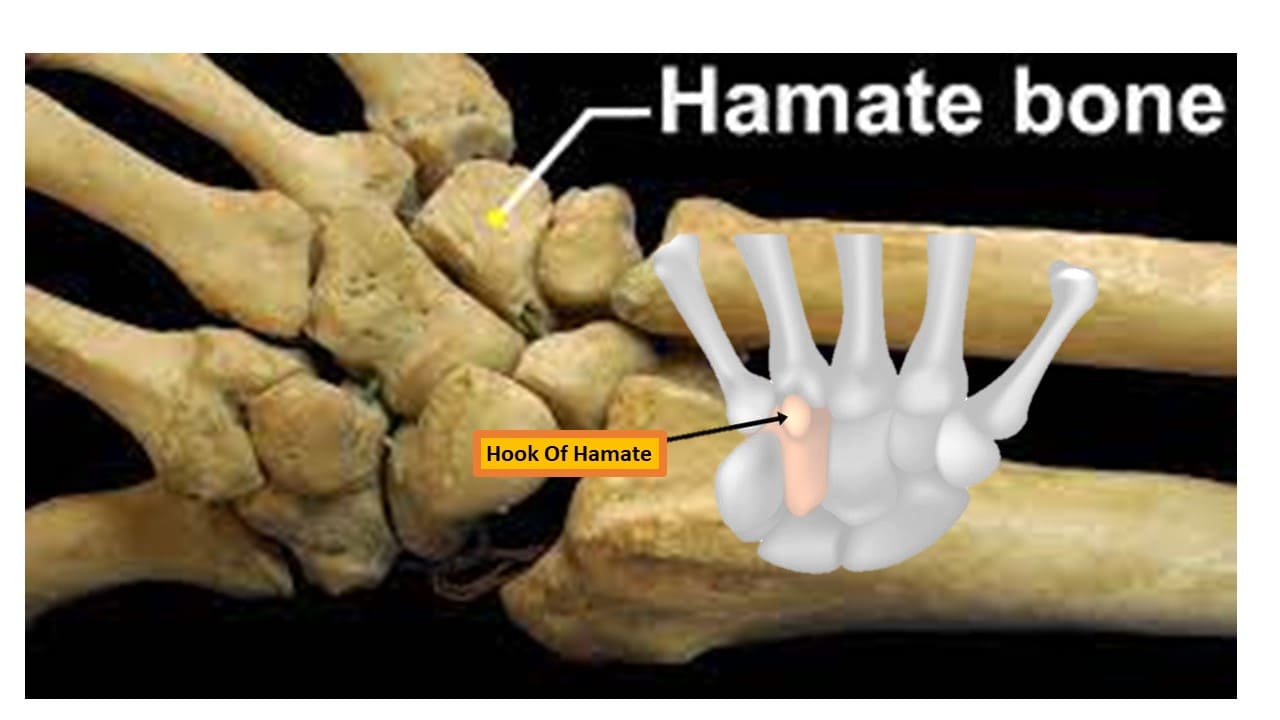
Hamate (“hooked bone”) is a wedge-shaped bone. It articulates with five carpal bones; the 4th and 5th metacarpals, the capitate, and the triquetrum. The hamate is easily distinguishable due to its shape and a hook-like process that extends towards the palmar surface.
The hamate bone is the most frequently fractured bone when a golfer hits the surface hard with a golf club on the downswing. Clinically, this may present with pain and symptoms of ulnar nerve damage; numbness and weakness of flexion in the 4th and 5th fingers. In a similar fashion to the scaphoid, the hook of the hamate is vulnerable to avascular necrosis due to its poor blood supply.
The Carpal Tunnel
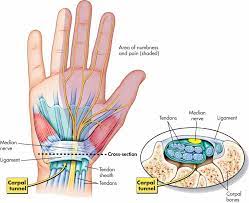
The carpal bones form a U-shaped arrangement which is directed anteriorly. The flexor retinaculum spans this U-shaped area to maintain the alignment of the carpal bones.
The medial side of the base of the arch is formed by the pisiform and hook of the hamate. The lateral side of the base of the arch is formed by the scaphoid and trapezium.
The flexor retinaculum attaches laterally to the trapezium and scaphoid bones and medially to the hamate and pisiform bones. Both the carpal bones and the flexor retinaculum form the carpal tunnel– the bones forming the wall and floor and the tendon, the roof.
Thickening of the flexor retinaculum can result in carpal tunnel syndrome which results in symptoms secondary to compression of the median nerve.

