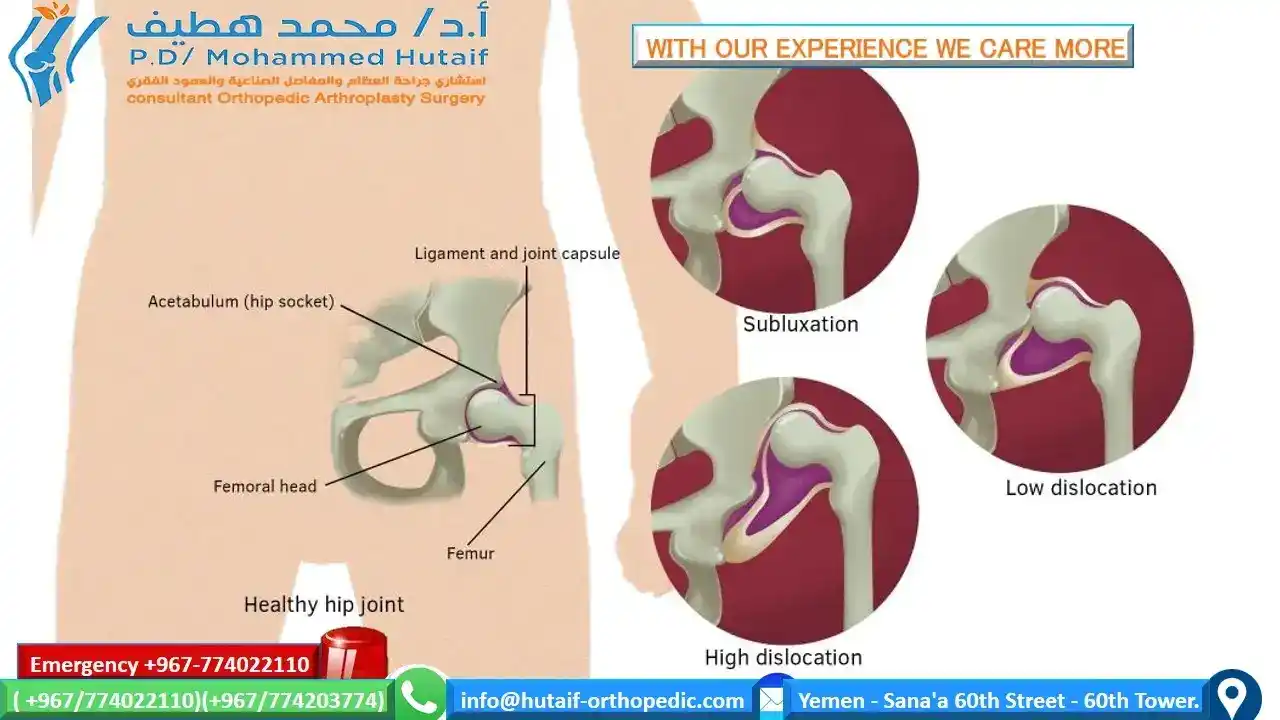
Hip Dysplasia-summary-NATURAL HISTORY
Developmental Dislocation (Dysplasia) of the Hip (DDH)-summary-NATURAL HISTORY
NATURAL HISTORY
IN This Artical
next page:
Get comprehensive information on orthopedic trauma and related health issues. Learn about different trauma procedures and treatment options.
Discover expert insights on shoulder and elbow conditions, treatments, and surgical techniques. Enhance your knowledge in this area.
Learn about orthopedic reconstruction procedures and techniques. Find out how these procedures can help in restoring functionality and improving quality of life.
Dive into the fundamentals of orthopedics with comprehensive information on the basic sciences behind the field. Enhance your understanding of orthopedics.
Access a collection of teaching cases that cover a wide range of orthopedic conditions and scenarios. Sharpen your diagnostic skills and learn from real-life cases.
Get valuable insights on spinal conditions, treatments, and surgical approaches. Stay updated with the latest advancements in spinal care.
Learn about different surgical approaches used in orthopedics. Understand the principles and techniques behind these approaches.
Test your knowledge in orthopedics with our collection of free multiple-choice questions. Challenge yourself and enhance your understanding.
Explore various surgical techniques used in orthopedics. Stay informed about the latest advancements and developments in this field.
Gain insights into surgical techniques specifically focused on pediatric orthopedics. Learn about procedures and treatment options tailored for younger patients.
Learn about the importance of a thorough physical examination in orthopedics. Discover techniques and tips for conducting a comprehensive assessment. Enhance your examination skills.
Test your orthopedic knowledge with our collection of MCQs. Challenge yourself and assess your understanding in various areas of orthopedics.
Prepare for the Chinese Graduating Exam in orthopedics. Get access to resources and study materials to help you succeed in the exam.
Explore surgical techniques specifically related to sports injuries and conditions. Learn about procedures tailored for athletes and sports enthusiasts.
Gain insights into operative techniques used in hand, wrist, and elbow surgeries. Learn about procedures and treatment options for conditions in these areas.
Stay tuned for new updates and developments in orthopedics. Explore upcoming features, resources, and information that will be available soon.
Understand musculoskeletal tumors and their treatment options. Learn about different types of tumors and available treatment approaches.
Access comprehensive information on foot and ankle conditions, treatments, and surgical techniques. Learn how to manage and treat various foot and ankle issues.
Explore the Chinese section of our website tailored for Chinese-speaking individuals. Find resources, information, and study materials specific to the Chinese orthopedic community.